What Are Some Of The Possible Services That A Link-layer Protocol Can Offer To The Network Layer
Network Devices:
HUB

Hub is one of the bones icons of networking devices which works at physical layer and hence connect networking devices physically together. Hubs are fundamentally used in networks that usetwisted pair cabling to connect devices. They are designed to transmit the packets to the other appended devices without altering any of the transmitted packets received. They act as pathways to directly electrical signals to travel along. They transmit the data regardless of the fact if data bundle is destined for the device continued or not.
Hub falls in 2 categories:
Active Hub: They are smarter than the passive hubs. They not only provide the path for the information signals infact they regenerate, concentrate and strengthen the signals before sending them to their destinations. Active hubs are as well termed as 'repeaters'.
Passive Hub: They are more like betoken contact for the wires to congenital in the concrete network. They have nothing to practise with modifying the signals.
Ethernet Hubs
Information technology is a device connecting multiple Ethernet devices together and makes them perform the functions every bit a single unit of measurement. They vary in speed in terms of data transfer rate. Ether utilizes Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Notice (CSMA/CD) to control Media access. Ethernet hub communicates in half-duplex mode where the chances of information collision are inevitable at well-nigh of the times.

Switches
Switches are the linkage points of an Ethernet network. Just equally in hub, devices in switches are connected to them through twisted pair cabling. Only the departure shows up in the manner both the devices; hub and a switch care for the data they receive. Hub works past sending the data to all the ports on the device whereas a switch transfers it just to that port which is continued to the destination device. A switch does so by having an in-congenital learning of the MAC address of the devices connected to information technology. Since the transmission of information signals are well divers in a switch hence the network operation is consequently enhanced. Switches operate in full-duplex manner where devices tin can send and receive data from the switch at the simultaneously unlike in half-duplex mode. The transmission speed in switches is double than in Ethernet hub transferring a 20Mbps connection into 30Mbps and a 200Mbps connection to go 300Mbps. Operation improvements are observed in networking with the extensive usage of switches in the modern days.

The following method will elucidate further how information manual takes place via switches:
- Cut-through transmission: It allows the packets to exist forwarded equally soon as they are received. The method is prompt and quick but the possibility of error checking gets overlooked in such kind of packet data transmission.
- Store and forward: In this switching environment the unabridged packet are received and 'checked' earlier being forwarded ahead. The errors are thus eliminated earlier being propagated further. The downside of this procedure is that error checking takes relatively longer time consequently making it a chip slower in processing and delivering.
- Fragment Free: In a fragment gratis switching surroundings, a greater part of the parcel is examined so that the switch tin can determine whether the packet has been caught upward in a collision. After the collision condition is determined, the package is forwarded.
Bridges
A bridge is a computer networking device that builds the connection with the other bridge networks which utilise the aforementioned protocol. Information technology works at the Data Link layer of the OSI Model and connects the dissimilar networks together and develops advice between them. It connects two local-area networks; two concrete LANs into larger logical LAN or two segments of the aforementioned LAN that employ the aforementioned protocol.

Autonomously from edifice upwardly larger networks, bridges are likewise used to segment larger networks into smaller portions. The bridge does so by placing itself between the two portions of two concrete networks and controlling the flow of the data between them. Bridges nominate to forward the information afterward inspecting into the MAC address of the devices connected to every segment. The forwarding of the data is dependent on the acknowledgement of the fact that the destination address resides on some other interface. It has the capacity to block the incoming menses of data every bit well. Today Learning bridges have been introduced that build a list of the MAC addresses on the interface by observing the traffic on the network. This is a leap in the development field of manually recording of MAC addresses.
Types of Bridges :
There are mainly three types in which bridges tin can be characterized:
- Transparent Bridge: Every bit the proper name signifies, it appears to be transparent for the other devices on the network. The other devices are ignorant of its being. It only blocks or forwards the information as per the MAC address.
- Source Route Span: It derives its proper noun from the fact that the path which bundle takes through the network is implanted inside the packet. It is mainly used in Token band networks.
- Translational Span: The procedure of conversion takes identify via Translational Bridge. It converts the information format of i networking to another. For instance Token band to Ethernet and vice versa.
Switches superseding Bridges:
Ethernet switches are seen to be gaining trend as compared to bridges. They are succeeding on the business relationship of provision of logical divisions and segments in the networking field. Infact switches are being referred to as multi-port bridges because of their advanced functionality
Routers
Routers are network layer devices and are particularly identified as Layer- 3 devices of the OSI Model. They process logical addressing information in the Network header of a parcel such as IP Addresses. Router is used to create larger complex networks by complex traffic routing. Information technology has the ability to connect unlike LANs on the same protocol. Information technology also has the ability to limit the flow of broadcasts. A router primarily comprises of a hardware device or a organization of the computer which has more than than i network interface and routing software.

Functionality:
When a router receives the information, information technology determines the destination address by reading the header of the packet. In one case the address is adamant, it searches in its routing table to get know how to reach the destination and and then forwards the parcel to the college hop on the route. The hop could exist the last destination or some other router.
Routing tables play a very pivotal part in letting the router makes a conclusion. Thus a routing table is ought to be updated and consummate. The two means through which a router can receive data are:
- Static Routing: In static routing, the routing information is fed into the routing tables manually. Information technology does non just get a time-taking job but gets prone to errors likewise. The manual updating is also required in case of statically configured routers when alter in the topology of the network or in the layout takes place. Thus static routing is feasible for tinniest environments with minimum of ane or 2 routers.
- Dynamic Routing: For larger environment dynamic routing proves to exist the practical solution. The process involves use of peculiar routing protocols to concur communication. The purpose of these protocols is to enable the other routers to transfer information about to other routers, and so that the other routers can build their ain routing tables.
Brouters
Brouters are the combination of both the bridge and routers. They have up the functionality of the both networking devices serving every bit a bridge when forwarding information betwixt networks, and serving as a router when routing information to individual systems. Brouter functions as a filter that allows some information into the local network and redirects unknown data to the other network.
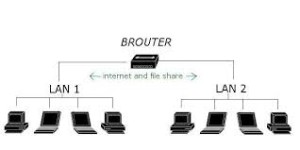
Brouters are rare and their functionality is embedded into the routers functioned to human action as bridge likewise.
Gateways
Gateway is a device which is used to connect multiple networks and passes packets from one packet to the other network. Interim equally the 'gateway' betwixt different networking systems or computer programs, a gateway is a device which forms a link betwixt them. It allows the reckoner programs, either on the aforementioned computer or on different computers to share data across the network through protocols. A router is as well a gateway, since it interprets information from one network protocol to another.

Others such as bridge converts the data into different forms between 2 networking systems. Then a software application converts the data from one format into some other. Gateway is a viable tool to translate the data format, although the data itself remains unchanged. Gateway might be installed in some other device to add together its functionality into another.
Network menu
Network cards likewise known every bit Network Interface Cards (NICs) are hardware devices that connect a computer with the network. They are installed on the mother board. They are responsible for developing a physical connexion between the network and the computer. Computer data is translated into electrical signals send to the network via Network Interface Cards.

They can as well manage some important data-conversion function. These days network cards are software configured unlike in olden days when drivers were needed to configure them. Fifty-fifty if the NIC doesn't come upward with the software so the latest drivers or the associated software can be downloaded from the internet every bit well.
Network protocols
Network protocols define a language of instructions and conventions for communication between the network devices. It is essential that a networked computer must take one or more protocol drivers. Usually, for two computers to interconnect on a network, they must use identical protocols. At times, a computer is designed to use multiple protocols. Network protocols similar HTTP, TCP/IP offer a footing on which much of the Cyberspace stands.
System requirement:
- The bus compatibility should be verified on installing an NIC into the system. The unremarkably used motorbus system is Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
- Memory I/O addresses and IRQ are needed.
- Need of drivers if non already installed.
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
ISDN are used to send over graphic or audio data files. It is a WAN technology that can be used in place of a dial up link. The accessibility of ISDN depends upon the provision of the service past the service provider, the quality of the line set up to your area. It surely provides higher speed than a modem and has the capability to pick upwards the line and driblet it considerably at a faster rate.

ISDN can create numerous communication routes on a single line. Present, fifty-fifty faster and cheaper technologies that ISDN have institute their way in the realm of technology.
Modems
Modem is a device which converts the figurer-generated digital signals of a figurer into analog signals to enable their travelling via telephone lines. The 'modulator-demodulator' or modem can be used every bit a dial up for LAN or to connect to an Internet access provider. Modems can be both external, as in the device which connects to the USB or the serial port of a estimator, or proprietary devices for handheld gadgets and other devices, as well as internal; in the form of add together-in expansion cards for computers and PCMCIA cards for laptops.

Configuration of a modem differs for both the external and internal modem. For internal modems, IRQ – Interrupt request is used to configure the modem along with I/O, which is a retention address. Typically before the installation of congenital-in modem, integrated serial interfaces are disabled, simultaneously assigning them the COM2 resources.
For external connectedness of a modem, the modem assigns and uses the resources itself. This is specially useful for the USB port and laptop users as the non-complex and simpler nature of the procedure renders it far much more beneficial for daily usage.
Upon installation, the second footstep to ensure the proper working of a modem is the installation of drivers. The modem working speed and processing is dependent on two factors:
- Speed of UART – Universal Asynchronous Receiver or Transmitter fleck (installed in the computer to which the modem connection is fabricated)
- Speed of the modem itself
Network Devices Quiz
Quiz i
Quiz ii
Quiz 3
Quiz 4
Quiz 5
Read more:
- What skills y'all need to laissez passer CCNA exam
- The Cisco Three Layer Bureaucracy Model
- Ethernet Cabling
- Ethernet Networking
- Data Encapsulation
- OSI Layer Model
- Network Topology
- Networking Essentials
- Estimator Networking
Free Cisco CCNA Study Guide
Free Practice Tests
- Free MTA Practice Tests and Exams
- Complimentary MCSA Windows 7 Do Tests and Exams
- Free MCSA Windows 8 Practice Tests and Exams
- Gratuitous MCSE and MCSA Windows Server 2012 Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA A+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- A+ Practice Test
- Complimentary CompTIA CDIA+ Certification Do Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Linux+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Complimentary CompTIA Network+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Project+ Certification Exercise Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Security+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Gratuitous CompTIA Server+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Gratuitous CompTIA Storage+ Certification Do Tests and Exams
- Free CCENT 100-101 ICND1, CCNA 200-101 ICND2, 200-120 CCNA Practice Exams and Tests
- Free Cisco CCNA certification practise tests and Exams Questions
- Free CCNA Security Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Gratuitous CCNA Wireless Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCNA Voice Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCNP exercise tests and Exams Questions
- Gratis CCIE Collaboration Certification Practise Tests and Exams
- Free CCIE Routing and Switching Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCIE Security Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCIE Wireless 350-050 Practice Exam
Router Admin Access IP Addresses
- 192.168.8.ane
- 192.168.100.1
- 192.168.254.254
- 192.168.l.2
- 192.168.15.1
- 192.168.0.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.0.2
- 192.168.1.4
- 192.168.three.1
- 198.162.1.one
- 192.168.11.i
Source: https://www.certiology.com/computing/computer-networking/network-devices.html
Posted by: edgertonwasmand.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are Some Of The Possible Services That A Link-layer Protocol Can Offer To The Network Layer"
Post a Comment